ImiRP User Guide
Table of contents
Create a new project
ImiRP can be used to generate mutants for microRNA recognition elements (MRE) in a nucleotide sequence of interest while ensuring that new MREs are not introduced in the process. To do this, it is first necessary to create a new project, input a sequence of interest, specify the species of interest, and specify the MREs to be mutated.
Project description
To use the ImiRP web application, go to imirp.org. Click on the Launch ImiRP tool at the top of the screen, and then select “Create New Project” from the Projects drop-down menu. To create a new project, first provide a project name (mandatory) and a description of the project (optional).
Sequence input
Next, click on the “Sequence Input” tab of the “Create Project” menu, input the sequence to be mutated and select the species of interest. ImiRP will accept DNA or RNA sequences, and the input sequence is then displayed above the create project tabs. To indicate the species, begin typing the scientific name or three letter organism code into the “Species” text box. All species having miRNA sequences available in miRBase version 22are available for selection.
Target sites
Use the “Target sites” tab of the “Create Project” menu to specify the MREs into which nucleotide substitutions will be introduced. Identify the nucleotide start positions of the 6mer “core” for each MRE to be mutated within the input sequence. For each MRE, this represents the nucleotide that is complementary to position 7 of the targeting miRNA.
| miRNA | Site type | MRE sequence | 3'UTR positions |
|---|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-7-5p | 8mer+G:U | GTTTTCCA | 17-22 |
| mmu-miR-9 | 6mer | CCAAAG | 21-26 |
| mmu-miR-376c | 7mer-m8+G:U | TTAACAGA | 45-50 |
| mmu-miR-450b-5p | 7mer-A1 | TGCAAAA | 50-55 |
| mmu-miR-129-5p | 8mer | GCAAAAAA | 52-57 |
| mmu-miR-329 | 6mer | GTGTGT | 104-109 |
Type the MRE start positions into the “mutation sites” text box to specify the sites to mutate. The region of the predicted MRE complementary to miRNA positions 2-7, called the mutation site, will be bolded in the displayed input sequence. Also, the input sequence position of the start and end of the defined mutation site will be represented in (x, y) format, where x is the first and y is the last nucleotide of the mutation site. This process can be repeated to specify multiple mutation sites per input sequence. Mutation sites can be removed by clicking the X. Click the “Create project” button to begin specifying mutation parameters.
Define mutation parameters
Once a project has been created, the user is directed to the project page where a mutation request can be submitted. The navigation menu on the left side of the project page presents “Overview”, “Mutate” and “Results” options.
The “Overview” option on the project page provides a summary of the information that was input when the project was created. It also provides information about any mutation requests that have been submitted. If a mutation request has not been submitted yet, the number “0” appears on the mutation request tab and no information will be available for viewing.
The “Mutate” menu option can be used to submit a mutation request for the created project. Once a mutation request has been submitted, results can be accessed using the “Results” menu.
Create a mutation request
In the “Mutate” menu, the desired mutation strategy and the invalid MRE site types can be defined. The “Mutation strategy” tab allows the user to define the nucleotides that can be used for introducing substitutions into the mutation sites. Using the drop-down menu, the user can also specify the number of consecutive nucleotide changes required per mutation site. The program defaults to introducing 2 consecutive nucleotide substitutions per mutation site, using only the nucleobase “G”.
Next, the “Define Invalid Sites” tab enables the user to specify the MRE types that they want to avoid creating upon mutation of the defined mutation sites. By clicking on the target site classes listed in the “Invalid site types” and “Valid site types” lists, and using the arrow buttons, users can move target site types between the two lists. Only mutations that do not create new invalid MRE types will be output in the results. However, any MRE types listed as valid may be created upon mutation.
Once mutation parameters have been defined, clicking the “Submit Mutation Request” button will begin the generation of mutant sequences that satisfy the input criteria. The user will be directed to the results menu within the project page.
Construct a final mutant sequence
Mutation sites and corresponding mutations are displayed in the results menu.
Select desired mutation(s)
Mutation sites are grouped based on inter-site spacing, with sites spaced less than 7 nucleotides apart being grouped into a single “Region”. This is performed because 8mer MREs are the largest recognized sites. Therefore, MREs spaced more than 7 nucleotides apart can be mutated without generating a new MRE that spans both mutations. The nucleotide position of each region is defined based on the start and end positions of the first and last sites in the region, and the mutation sites are displayed in square brackets.
A maximum of five mutations that satisfy the input mutation criteria will be displayed per region. For each region display box, the original input sequence is displayed above, and the mutated sequences are listed below.
To select the desired mutant sequence for each region from the list, click on the select bubble to the left of the mutant sequence. One mutant sequence can be selected per region. As mutant sequences are selected for each region the region display box will change green and the “Assembled Mutant Sequence” displayed below will be updated to include the specified nucleotide substitutions.
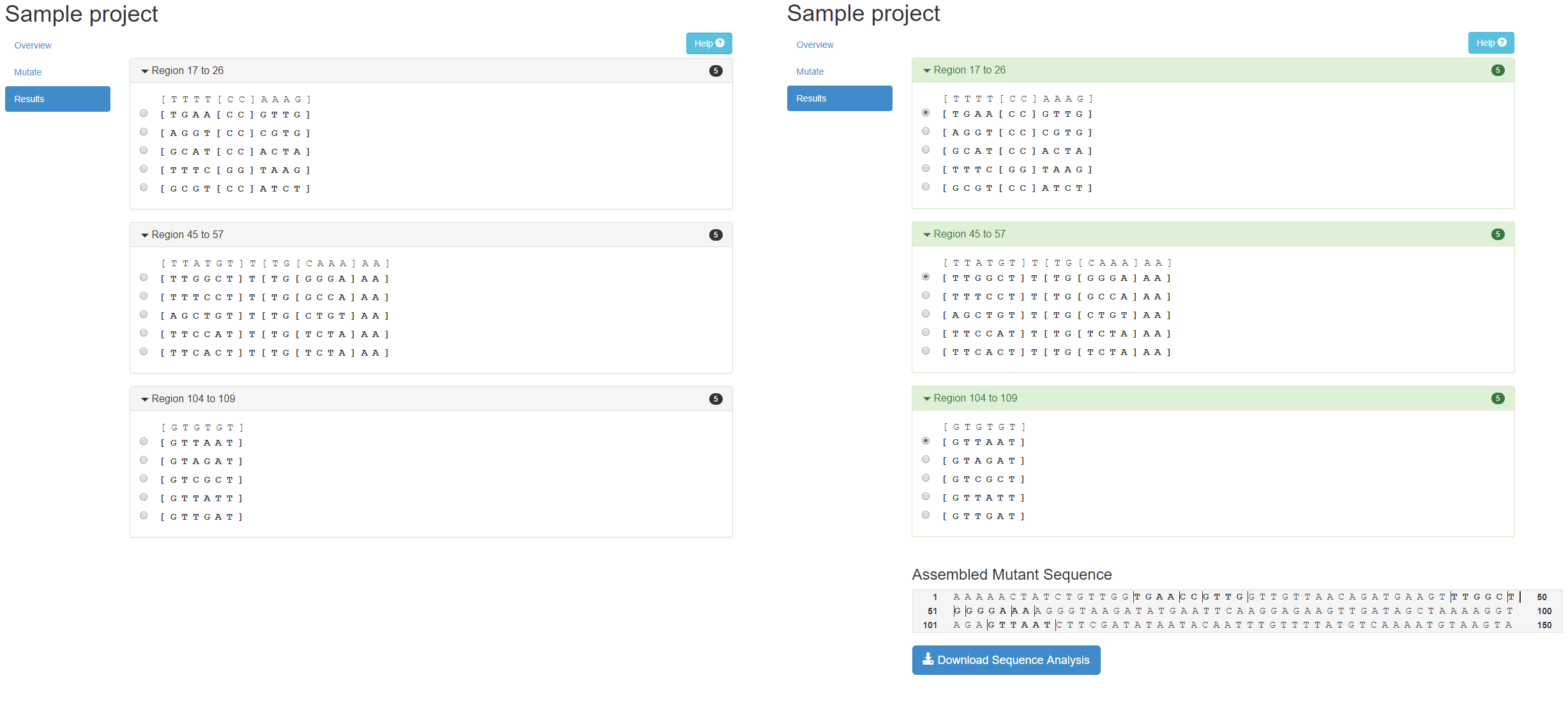
Once one mutant sequence has been selected per region, clicking the “Download Sequence Analysis” button will enable the user to download a ZIP folder, entitled mutant_analysis.zip, containing a single TXT file and three CSV files. The TXT file contains the project information, input sequence and final mutant sequence. The CSV files contain information about the predicted MREs in the input sequence, predicted MREs in the mutant sequence, and all predicted MREs that have been newly created in the mutant sequence.
Summary and submit new request
Returning to the overview menu reveals that one mutation request has now been submitted, and provides information about the mutation parameters, the total number of mutants generated, and the number of valid mutants generated.
If the mutation criteria are too stringent and successful (i.e. valid) mutations are not generated, returning to the mutate menu within the project page will enable to user to specify new mutation parameters and submit a new mutation request.